Project #1
Calibrating satellite imagery with on-the-ground plant & soil factors.
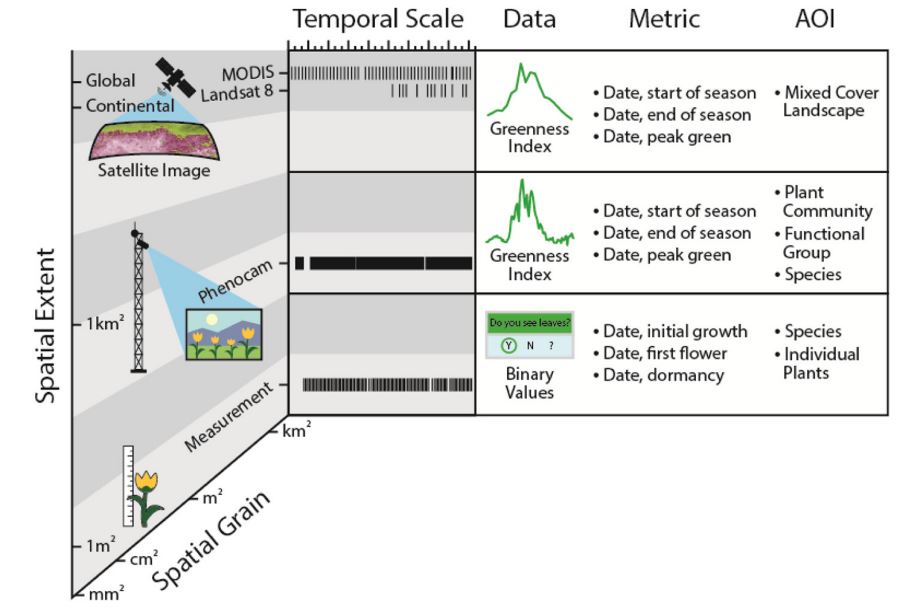
Research Objective
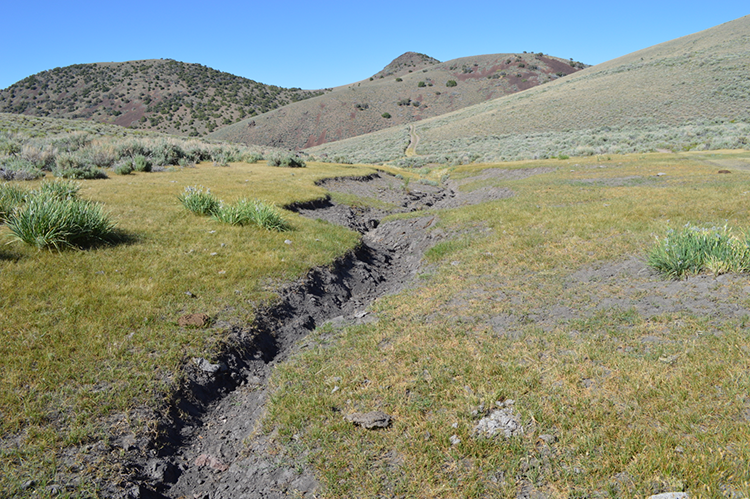
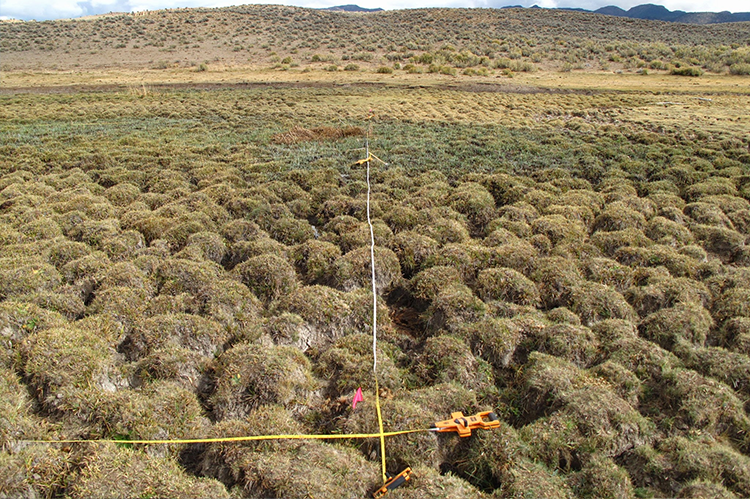
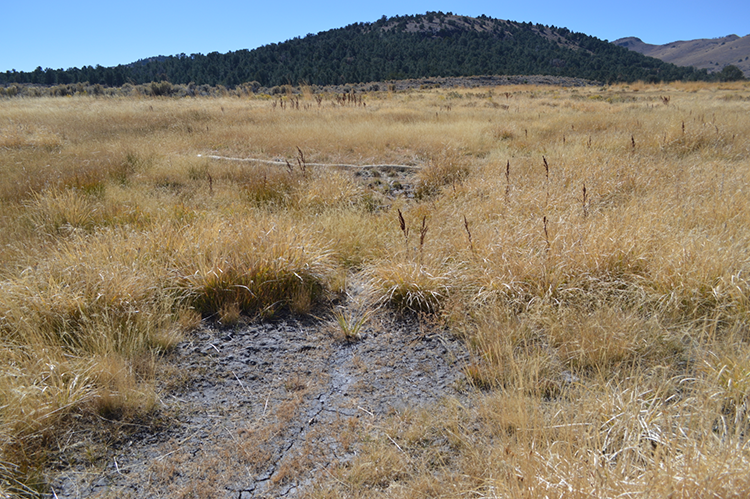
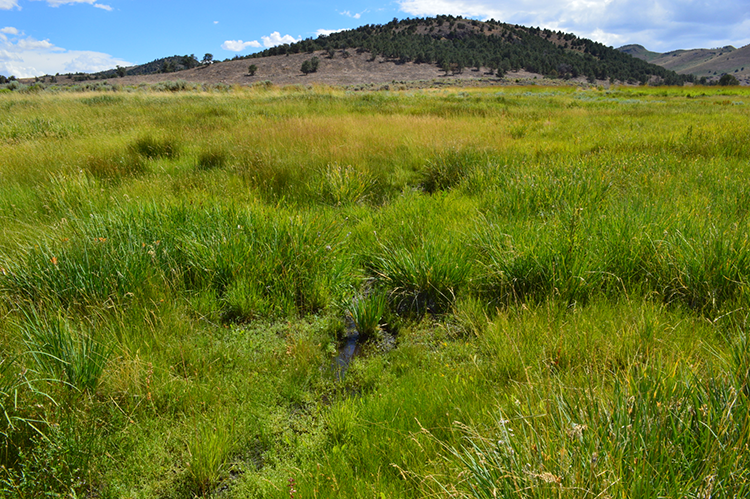
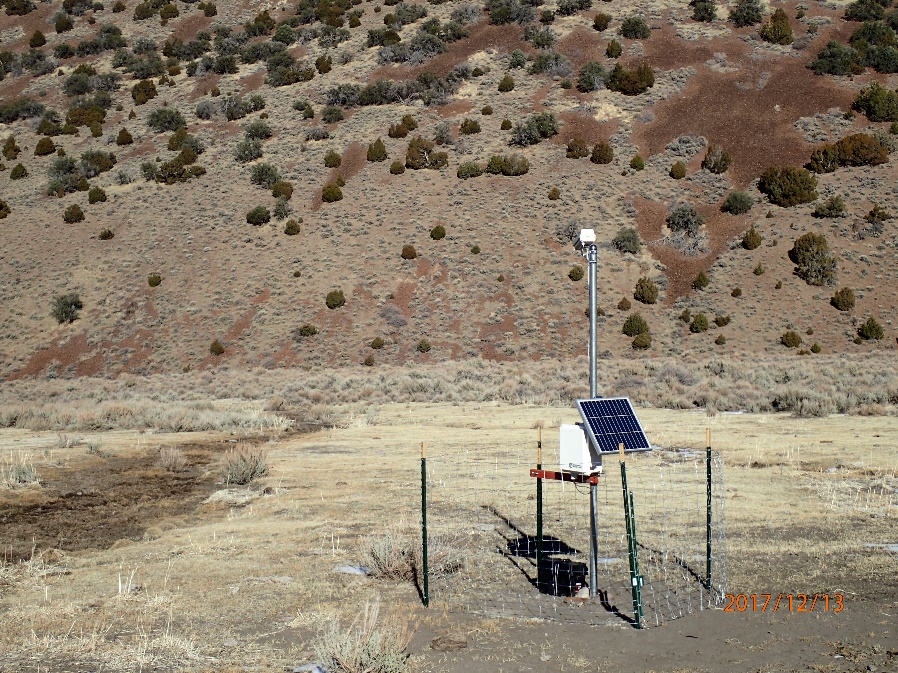
- Create 3 conditions within a fenced 1-acre area adjacent to a natural spring
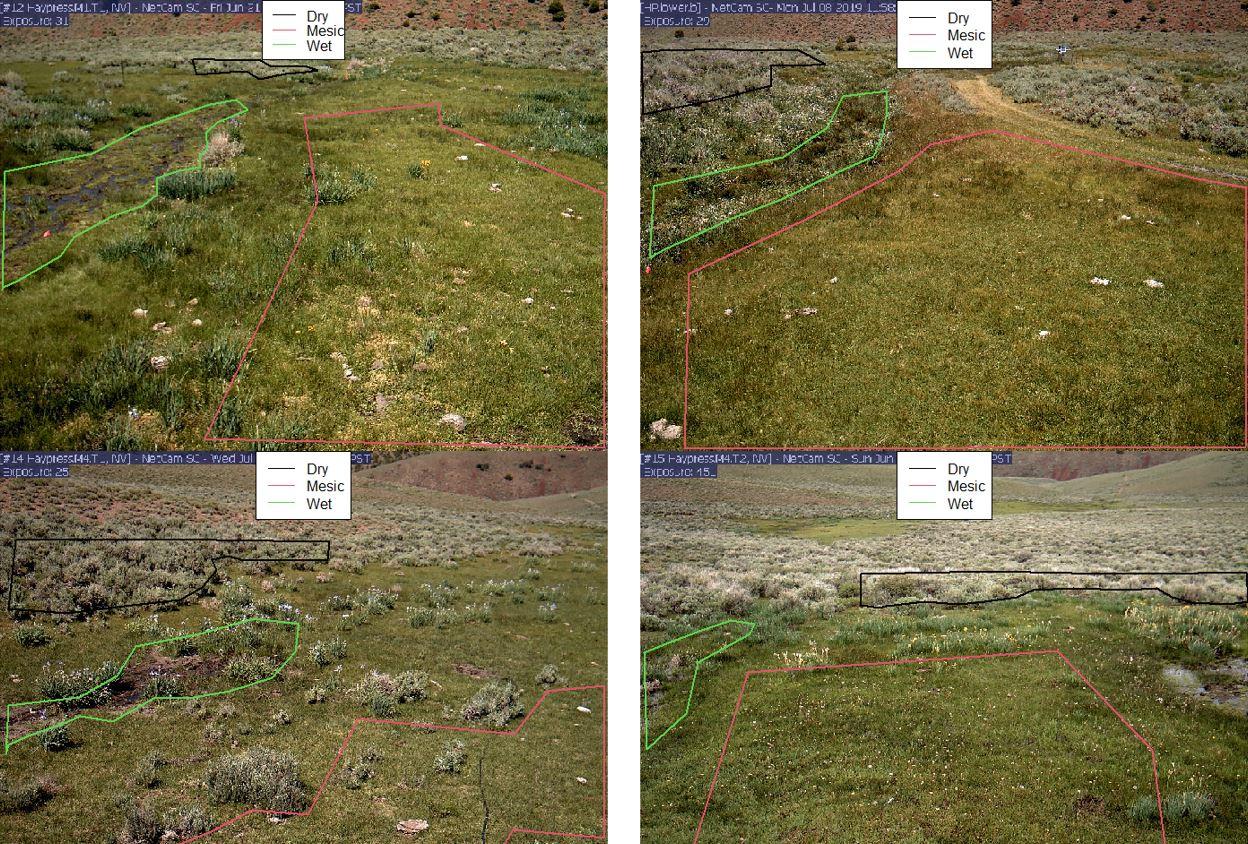
- Measure soil colour, redox, carbon, CO2 fluxes, plant condition, soil cover
- Calibrate measured factors with satellite imagery
Relevance
- The ability to remotely measure plant and soil conditions over large and often hard-to-access areas using satellite imagery will be an important tool in the fight against desertification globally.